🚀 Cache Me If You Can
A comprehensive, production-ready microservice project designed to teach Redis caching patterns through hands-on experience. Features FastAPI backend, PostgreSQL database, Redis cache, and an interactive Astro frontend with real-time performance metrics.
Perfect for learning cache-aside patterns, Docker orchestration, and microservice architecture in a realistic development environment.
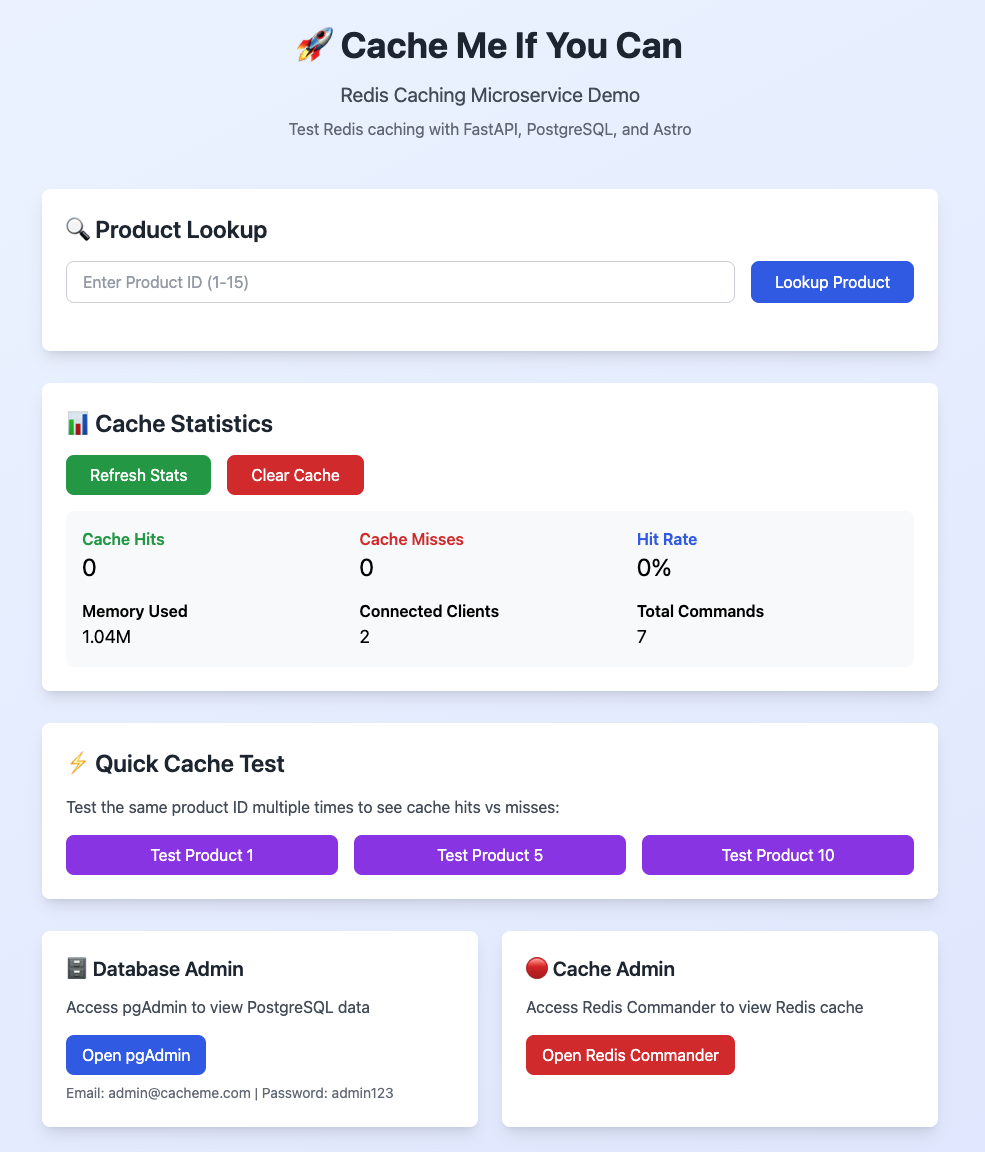 The main testing interface with real-time performance metrics and cache statistics
The main testing interface with real-time performance metrics and cache statistics
🔧 Tech Stack
| Component | Tool/Framework | Version | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Backend | FastAPI + Uvicorn | Python 3.12.3 | RESTful API service |
| Database | PostgreSQL | 15.6 | Primary data store |
| Cache | Redis | 7.2.5 | High-performance caching layer |
| Frontend | Astro + Tailwind | Node 20.12.0 | Interactive testing interface |
| DB Admin | pgAdmin | 9.4 | PostgreSQL management UI |
| Cache Admin | Redis Commander | Latest | Redis visualization & management |
| Orchestration | Docker Compose | Latest | Service coordination |
🏗️ Architecture
┌──────────────────┐ GET /products/{id} ┌──────────────────┐
│ │──────────────────────→│ │
│ Astro Frontend │ │ FastAPI Backend │
│ (localhost:3000) │←──────────────────────│ (localhost:8000) │
│ │ 4. JSON + Metrics │ │
└──────────────────┘ └─────────┬────────┘
│
│ 1. Check Redis
│
┌─────────▼─────────┐
│ │
│ Redis Cache │
│ (localhost:6379) │
└─────────┬─────────┘
│
┌───────────┴───────────┐
│ │
✅ Cache Hit ❌ Cache Miss
│ │
(2ms response) │
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ │
│ PostgreSQL Database │
│ (localhost:5432) │
└──────────┬──────────┘
│
│ 2. Query DB
│ (50-200ms)
│
3. Cache result & return
🚀 Quick Start
Prerequisites: Docker (20.10+), Docker Compose (2.0+), ports 3000, 8000, 5432, 6379, 5050, 5540 available, 2GB+ RAM
1. Launch Services
# Start all services (first run will build images)
docker compose up -d --build
# Check all services are healthy
docker compose ps
2. Access Applications
| Service | URL | Credentials | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontend | http://localhost:3000 | None | Main testing interface |
| API Docs | http://localhost:8000/docs | None | Interactive API documentation |
| pgAdmin | http://localhost:5050 | admin@cacheme.com / admin123 |
Database management |
| Redis Commander | http://localhost:5540 | None | Cache visualization |
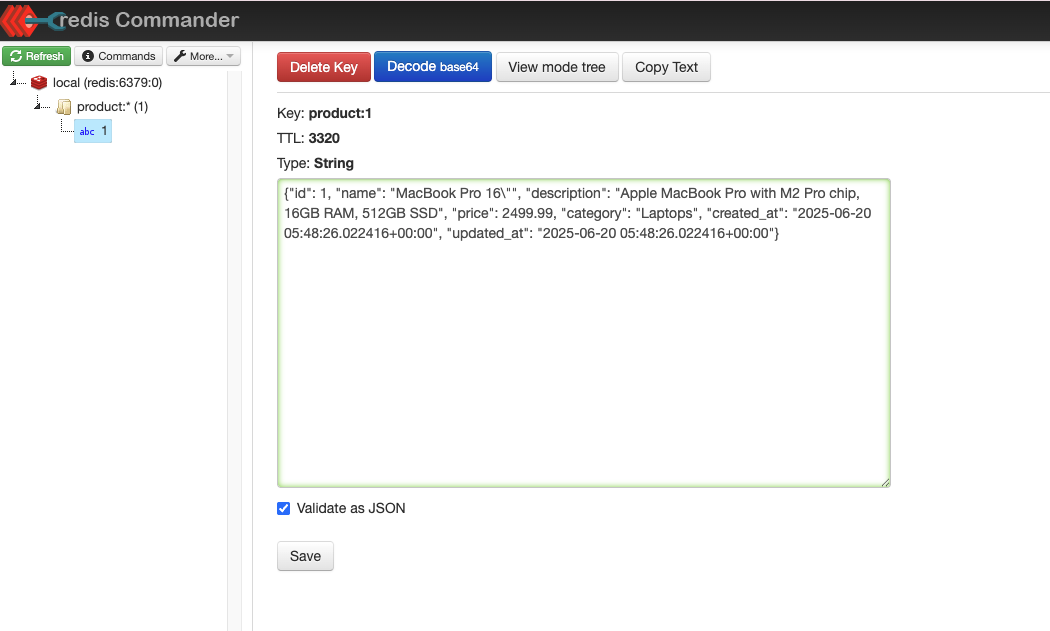 Redis Commander interface showing cached product keys, data types, and TTL information
Redis Commander interface showing cached product keys, data types, and TTL information
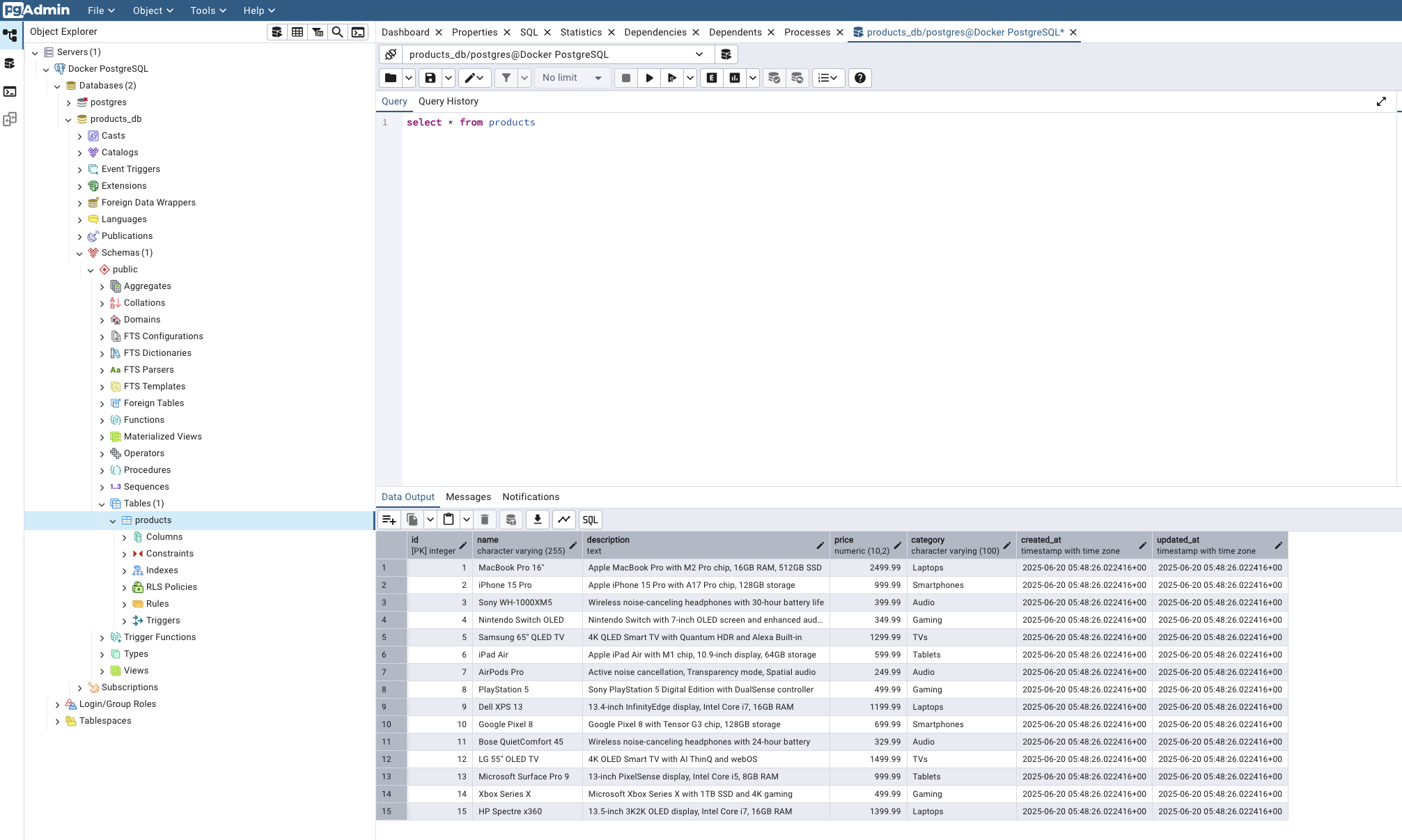 pgAdmin automatically configured with PostgreSQL connection and sample product data
pgAdmin automatically configured with PostgreSQL connection and sample product data
🎉 Everything is pre-configured! PostgreSQL initializes with 15 sample products, pgAdmin auto-connects to the database, and Redis Commander connects to the cache.
🧠 Understanding Redis Caching
What is Redis? Redis (Remote Dictionary Server) is an in-memory data structure store that serves as a database, cache, and message broker. Used by Twitter, GitHub, Instagram, and Snapchat.
🚨 The Problem Redis Solves
- Traditional Issue: Every user request hits the database directly
- Result: Slow response times, high server costs, poor user experience
- Redis Solution: Cache frequently accessed data in memory for instant retrieval
Real-World Use Cases:
- E-commerce: Product catalogs, user sessions, shopping carts
- Social Media: User profiles, news feeds, trending content
- Gaming: Leaderboards, player stats, game state
- Financial: Stock prices, exchange rates, account balances
- Content Delivery: Web pages, API responses, search results
Key Redis Advantages:
- 🚀 Speed: In-memory storage = microsecond response times
- 🗂️ Data Structures: Strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps
- ⏰ Smart Expiration: Automatic data cleanup with TTL
- 🔄 Persistence: Optional disk backup for data safety
- 📊 Monitoring: Built-in statistics and performance metrics
- 🔧 Atomic Operations: Thread-safe operations for concurrent access
Cache-Aside Pattern (Our Implementation):
- Application Request → User wants product data
- Check Cache First → Query Redis for cached product
- Cache Miss → If not found, query PostgreSQL database
- Cache Population → Store database result in Redis with TTL
- Cache Hit → Next request gets data instantly from Redis
- Performance Win → 10-100x faster response for subsequent requests
Business Impact:
- Performance: Sub-millisecond response times
- Scalability: Handle 10x more users with same infrastructure
- Cost Savings: Reduce database server requirements by 50-80%
- User Experience: Faster page loads = higher conversion rates
- Reliability: Less database load = fewer timeouts and errors
⚡ Performance & Features
💡 Local Environment Note: Response times vary by system, but you’ll always observe dramatic performance differences between cache hits and database queries.
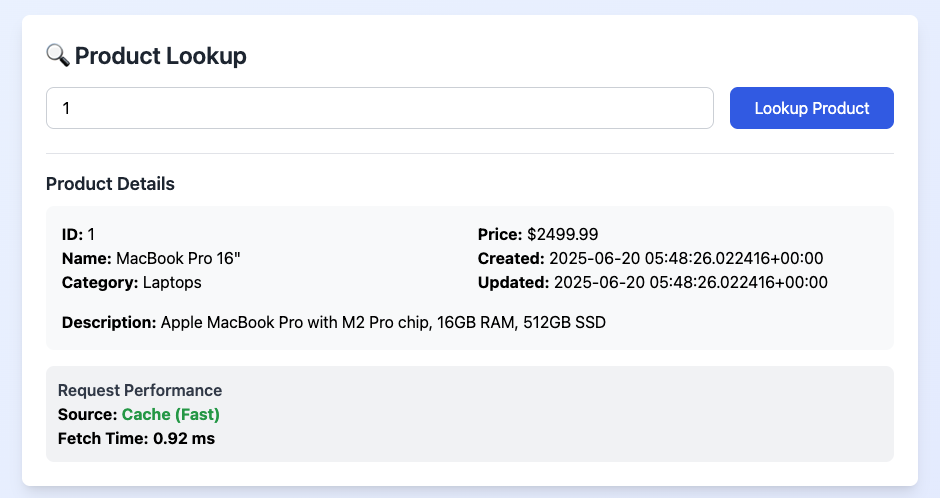
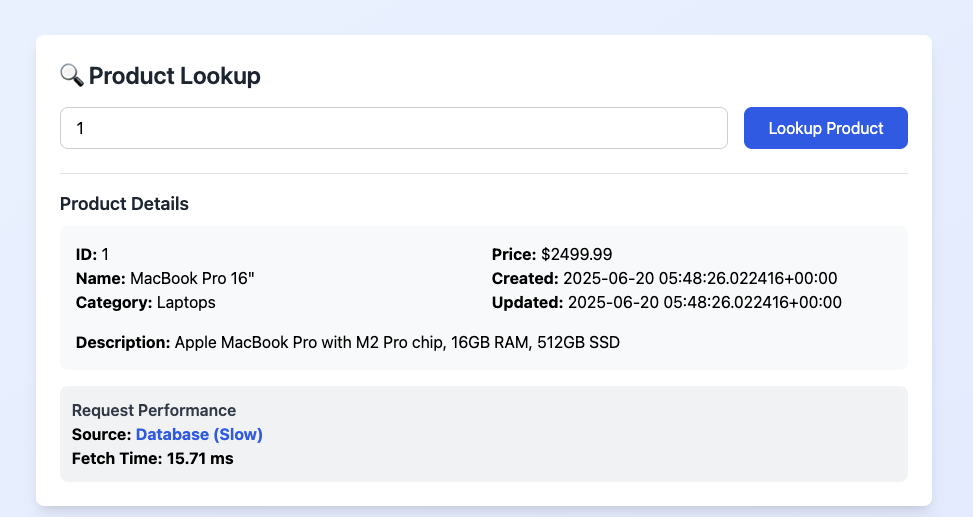 Redis cache hits vs PostgreSQL database queries - 5-50x performance improvement
Redis cache hits vs PostgreSQL database queries - 5-50x performance improvement
Performance Expectations:
| Scenario | Response Time | Source | Speed Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cache Hit | ~2-15ms | Redis | 5-50x faster |
| Cache Miss | ~20-300ms | PostgreSQL | Baseline |
Interactive Features:
- Product Lookup: Test individual products with real-time metrics
- Quick Test Buttons: One-click testing for products 1, 5, and 10
- Performance Tracking: Visual indicators for cache vs database responses
- Cache Management: Clear all cached data with one button
- Real-Time Metrics: Response time tracking, source identification, live statistics
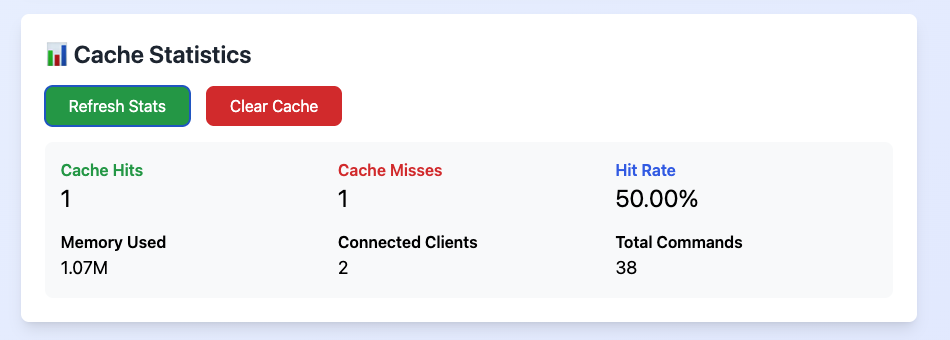 Live Redis cache statistics dashboard
Live Redis cache statistics dashboard
Key Performance Indicators:
- Cache Hits/Misses: Success vs fallback to database
- Hit Rate:
(Hits / (Hits + Misses)) × 100- Target 80%+ in production - Memory Usage: Current Redis memory consumption
- Connected Clients: Active connections (typically 2: backend + Redis Commander)
- Total Commands: All Redis operations since startup
🔧 API Reference
Core Endpoints:
GET /products/{id} # Get product with caching & metrics
GET /products # List all products (paginated)
GET /cache/stats # Redis cache statistics
DELETE /cache/clear # Clear all cached data
GET /health # Service health check
Product Response Format:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Wireless Headphones",
"category": "Electronics",
"price": 79.99,
"description": "High-quality wireless headphones...",
"created_at": "2024-01-01T00:00:00",
"updated_at": "2024-01-01T00:00:00",
"source": "cache", // "cache" or "database"
"fetch_time_ms": 2.45 // Processing time in milliseconds
}
Cache Statistics Response:
{
"cache_stats": {
"keyspace_hits": 42,
"keyspace_misses": 8,
"used_memory_human": "1.2M",
"connected_clients": 2,
"total_commands_processed": 156
}
}
🛠️ Management & Troubleshooting
Volume Management:
# List all project volumes
docker volume ls | grep cache-me
# Volume purposes:
# cache-me-postgres-data → Database files
# cache-me-redis-data → Cache persistence
# cache-me-pgadmin-data → Admin configuration
# cache-me-frontend-node-modules → Dependencies
# Complete reset (removes all data)
docker compose down -v
Common Issues & Solutions:
🔴 Services won’t start
# Check port conflicts
netstat -tulpn | grep -E ':(3000|8000|5432|6379|5050|5540)'
# View service logs
docker compose logs <service-name>
🔴 Database connection issues
# Reset database volume
docker compose down
docker volume rm cache-me-postgres-data
docker compose up -d
🔴 Cache not working
# Check Redis connectivity
docker compose exec backend redis-cli -h redis ping
# View backend logs
docker compose logs -f backend
🔴 pgAdmin server not auto-configured
# Reset pgAdmin configuration
docker compose down
docker volume rm cache-me-pgadmin-data
docker compose up -d
Performance Issues:
- Slow responses: Check Docker resource allocation (increase RAM/CPU)
- High memory usage: Clear cache via UI or restart Redis container
- Connection timeouts: Ensure all services are healthy:
docker compose ps
Monitoring:
# Follow all service logs
docker compose logs -f
# Monitor specific service
docker compose logs -f backend
# Check service health
docker compose ps
# Test API health
curl http://localhost:8000/health